Advanced Materials Letters, June 2020 issue on Researcher of the year for 2020: Professor Herbert Gleiter, Germany
Advanced Materials Letters (AML) is a leading non-profit open access, peer-reviewed international journal published by the International Association of Advanced Materials (IAAM). IAAM has continuously been promoting the not-for-profit Diamond Open Access journal publishing practices since June 2010. AML launched in June 2010 as the official journal of IAAM and publishes high-quality peer-reviewed articles on materials science, engineering, and technology. The journal provides a platform to present the latest research on both theoretical and experimental results as full papers, reviews, communication, letter to editors, etc. The subjects covered span through a wide range that includes materials of chemistry, physics, engineering, and technology for numerous applications.
In the month of June 2020, IAAM released the 6th issue of the 11th volume of Advanced Materials Letters. This issue contains editorial, review and research articles, a total of 13 documents including the editorial published on the “researcher of the year 2020 – Prof. Herbert Gleiter”. All the articles published in June 2020 can be downloaded for free at https://www.vbripress.com/aml/.
Editorial: Researcher of the year 2020 Professor Herbert Gleiter, Germany
The first article of this issue is the editorial, written by Prof. Ashutosh Tiwari, Editor-in-Chief of Advanced Materials Letters. The editorial is dedicated to Prof. Herbert Gleiter, who has been conferred upon with prestigious title “Researcher of the Year 2020” by IAAM. Prof. Gleiteris is a Director, Institute of Nanotechnology, Research Center Karlsruhe, Germany. Prof. Gleiteris is considered as a revolutionary researcher of the world of nanomaterials due to his pioneer work in nanoscience and nanotechnology. The editorial emphasizes his education, academic carriers, recognition, awards, contributions and along with his last 30 year’s groundbreaking work in nanoscience and nanotechnology has long-lasting effect on scientific enquiries.

Citation of the article: Adv. Mater. Lett., 2020, 11 (6), 20061520, Download Full article.
Review Article 1: Self-Sealing Polymeric Materials: Mechanism and Applications
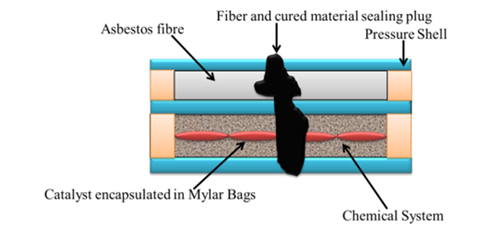
The second article review the research and development of self-sealing materials along with mechanism and applications. This article authored by the N. Kumar et al. from Defense Materials & Stores Research and Development Establishment, DMSRDE (DRDO), India. This work describes self-sealing phenomenon, sealant materials and their applications in various strategic materials and system namely self-sealing spacecraft structures in the meteoroid environment, fuel tank for fighter aircrafts, hemostatic syringe to prevent bleeding, and tires to prevent punchers and concrete structures to prevent water leakage. In addition, this article also describe that self-sealing approaches in the drug administration, cement crack repairing, and automobile industry area also being applied to avoid catastrophic failure and provide a new direction to the modern technology.
Review Article 2: Development of Ruthenium Complex based Sensitizers, Organic based Sensitizers, and Co-Sensitization System for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
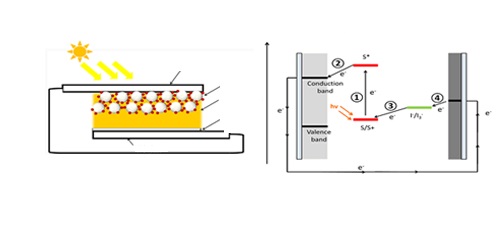
The third article of this issue is written by K.F. Chan with a group of author from Malaysia and China and they reviewed the recent development of different type of sensitizers such as ruthenium complex, organic, and co-sensitizers for dye sensitized solar cell. This review article reports the recent development in the molecular engineering of ruthenium sensitizers, organic chromophores, along with the study of the co-sensitization systems. This reports also highlighted that there are on-going efforts to achieve a wider absorption range for sensitizers, which includes the visible light, ultra-violet, and infrared red ranges and thus higher efficiencies. As a whole, the future prospects for thin film solar cell development will be directed toward achieving a low manufacturing cost, feasible real-life application, and minimum environmental pollution, while maintaining high performance.
Research Article 1: Characterization of a New Copper Paste for Printed Electronics
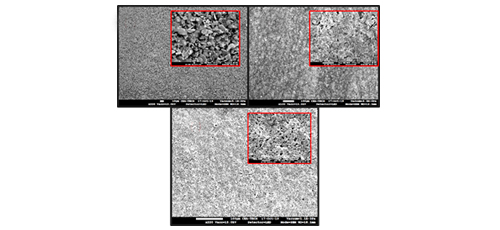
The fourth article of this issue is dedicated to the characterization of copper paste for printed electronics application and this article is written by I. Hendi et al. from CEA Tech, France. This article raise the point that printed electronics can be considered as an additive manufacturing technique allowing the fabrication of circuits and devices such as micro-electromechanical system (MEMS), sensors, and light emitting diodes (LED). This article reports the innovation by qualifying a paste that has a very good adhesion on a large variety of mechanical substrates and become conductive under laser activation, and its resistivity is also evaluated through four-probe method and results have been also compared with commercial pastes.
Research Article 2: Co-Ni Nanowires Arrays with Tunable Properties Obtained by Template Synthesis
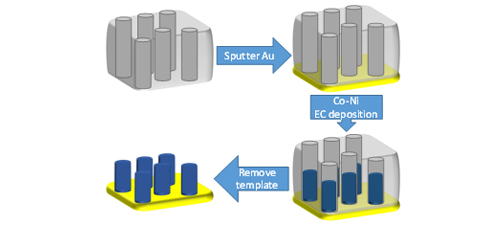
The fifth article of this issue is dedicated to the template synthesis of Co-Ni nanowires arrays with tunable properties. This article is written by a group of researcher from University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest, Splaiul Independentei, Romania and Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, University of California Davis, USA. In this article, nanowires arrays of Co-Ni were grown by electrochemical template synthesis from citrate solutions containing Co and Ni in order to achieve a higher Ni concentration in the alloy. These results provide the necessary information to construct Co and Ni-rich multi-segmented nanowires with tailored magnetic properties for an array of possible applications in electronics, photonics, and other fields.
Research Article 3: Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes using Polyvinylpyrrolidone for Application in Cement - based Composites to Enhance Electrical Conductivity
The sixth research article of this issue is focused on the study of to analyze the effective MWCNTs dispersion methods for the application in cement-based composites. This article is reported by G. Prateek et al. from Department of civil engineering and architecture, Wuyishan University, China. This article studies the integrated dispersion method and reported the comparative dispersion efficiency for two types of CNTs and three different types of surfactant. This article also studied the different composition (%) of CNTs, different ratio of CNT and surfactant, variable ultrasonic time span along with UV-vis spectroscopy, electrical resistivity measurement.
Research Article 4: Towards a Physics Based Model of Magnetic Barkhausen Noise in Steel
T.W. Krause et al. from department of physics and space science, Royal military college of Canada, Canada write seventh article of this issue. This article reported that ferromagnetic iron based alloys are used in many important steel products including electrical steels, oil and gas pipelines, naval structures, aircraft landing gear and automotive components while magnetic properties of these materials are vital too for direct implications for energy efficiency application such as electrical motors and transformers. This article also reports to develop the physical basis for Barkhausen noise generation under conditions of applied stress and in the presence of pinning.
Research Article 5: Sustainable Concept and Economic Evaluation of a Solar-Powered Hydrogen Generation Unit
Eighth article of this issue written by L. langenbucher et al. from Institute of Sustainable Energy Engineering and Mobility, University of Applied Science Esslingen, Germany. This article is focused on an overall energy consumption prediction for the area of Stuttgart city in Germany and a specific analysis of a solar-fed power-to-gas plant in an industrial area close to Stuttgart. This paper presents the advantages of large-scale industrial hydrogen production plants and analyses the techno-economic aspects of a subsequent hydrogen utilization in public transport. This article concluded that a sustainable concept of a solar-powered hydrogen generation unit is developed under the prospective premises of the Masterplan of Stuttgart.

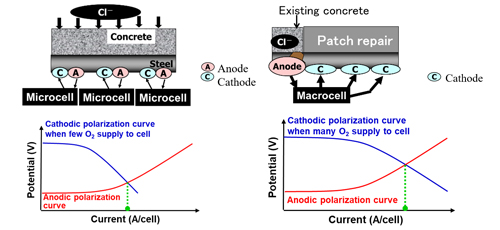
Research Article 6: Macrocell Corrosion and its Countermeasure for Reinforced Concrete after Patch Repair
Article number 9 of this issue underlined that reinforced concrete has been used in civil infrastructure development for several decades however chlorides easily corrode steel bars used in some concrete structures. This article is reported by Miyazato and Hanoka form department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Kanazawa Institute of Technology, Japan. This study analyzed the macrocell corrosion mechanism in reinforced concrete structure after a patch repair and to determine the influence of corrosion on structural performance. This study analyze the macrocell corrosion mechanism, as well as its rate, in a reinforced concrete with a joint after a patch repair process, using not only theoretically anodic and cathodic polarization curves but also experimentally specimens with special divided steel bars. Also, this study determines the influence of the extent of corrosion on the structural performance of a reinforced concrete beam. Finally, a method to control the macrocell corrosion is proposed.
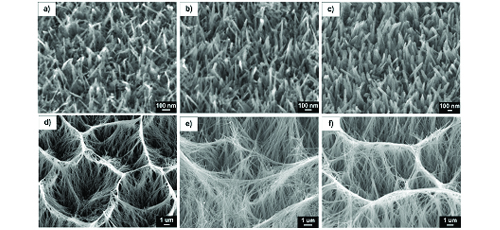
Research Article 7: Modelling the Height of Hydrothermally Synthesized Titanium Dioxide Nanostructures
Jaggessar and Yarlagadda write the tenth article of this issue from School of Mechanical and Processing Engineering and Institute of Health and Biomedical Innovation, Queensland University of Technology, Australia. This article raises the widespread concern about bacterial infection for medical community. This study develops statistical models between nanostructure height and NaOH concentration, reaction temperature and reaction duration. Quantitative representation of hydrothermal growth is important to the hydrothermal process, working to improve process efficiency and predict resulting material properties prior to fabrication. Finding of this study is significant for the designing of nanostructured surfaces for the antibacterial applications and users of the hydrothermal method for effective and efficient nanostructure fabrication.
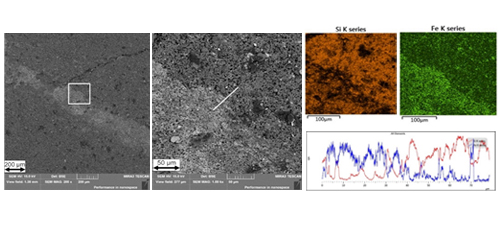
Research Article 8: Cellular SiC/Iron Alloy Composite
Article number eleventh of this reported that Cellular SiC/iron alloy composite with spatial structure and intersecting skeletons could have a promising spectrum of potential uses. This article written by B. Lipowska et al. from Institute of Ceramics and Building Materials Refractory Materials Division, Poland. This article presents a cellular SiC/iron alloy composite with a spatial structure of mutually intersecting networks through pressureless infiltration of porous ceramic preform with molten metal. The microstructure of the obtained composite sample is characterized while the contact between SiC and cast iron is also investigated.
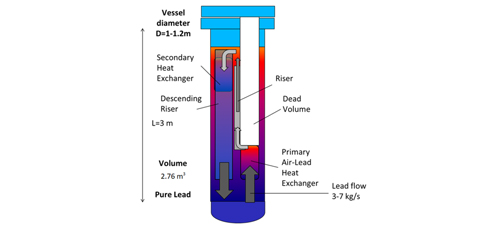
Research Article 9: Conceptual Design of the CSP Lead Demonstrator SOLEAD
The twelfth article of this issue is reported by a group of researcher from Italy. This article focused on the investigation the possibility of using liquid lead as heat storage medium for high-temperature thermal storage in concentrated solar power plant. This article reports the ENEA SOLEAD conceptual design developed in 2017, mainly constituted the Piping & Instrumentation Diagram, P&ID with the full lists of instrumentation and components and with the description of the main process of the facility, including basic operating procedures, the preliminary basic design (main dimensions/solutions to adopt) for the main components as the draining/storage tank, main vessel and the primary and secondary heat exchangers and the conceptual design of the data acquisition and control system, both for the acquisition and power panels.
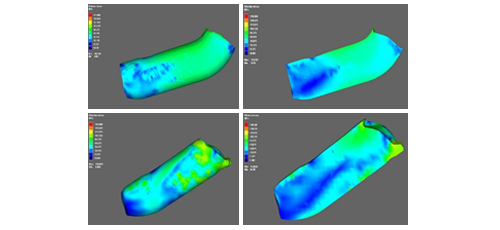
Research Article 10: Numerical and Experimental Analyses of Equal Channel Angular Processing of Pure Aluminum
The last article in this issue is published by W.H. El-Garaihy from Mechanical Engineering Department, College of Engineering- Unizah, Qassim University, Saudi Arabia. This article reports that equal channel angular processing is one of the most appealing and potentially efficient severe plastic deformation techniques for fabricating ultrafine grained and nanostructured material with sufficiently improved mechanical properties which has enabled this technique to be used in industrial sector. This study provide a more detailed mapping of the equal channel angular processing process through numerical modeling to study the effectively induced stress-strain behaviors and their distribution after multiple passes of equal channel angular processing of commercially pure aluminum. N addition, validation of the numerical model is also carried out by investigating the hardness distribution across the sample’s transverse section and microstructural observations after deformation.
All the articles published in this issue are available free to read at https://www.vbripress.com/aml/. International Association of Advanced Materials, IAAM invites all the members from advanced materials community to promote this not-for-profit Diamond Open Access Policy by submitting their articles or special issue proposal in the Advanced Materials Letters. The peer-review process of submitted articles in the Advanced Materials Letters is done by manuscript central, ScholarOne – Web of Science Group – Clarivate Analytics, USA. The researchers are invited to submit their manuscripts at ScholarOne manuscript submission system.
June 2nd, 2020 IAAM Blog International Association of Advanced Materials Leave a Comment
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Search
Recent Posts
- The 15th Anniversary of Advancing Materials
- Materials Triggered Towards Climate Neutral and Bio Active Functionality Via Nano and Electrochemical Interaction: Evolution of Advancement in the Volume 12 of Advanced Materials Letters, August 2021
- Promising Materials Features Transforming Sustainable Development with Intelligence and Green Chemistry: Exclusive Paradigm of the Volume 12 of Advanced Materials Letter, July 2021
- Attaining the SDGs Through Resilient Approach Needed High Performances Materials, Symbolize in the 6th Issue, Volume 12, June 2021 of Advanced Materials Letters